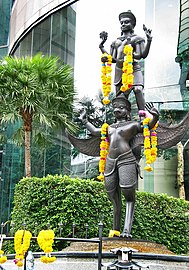Narayana

| Part of a series on |
| Vaishnavism |
|---|
 |
Narayana (Sanskrit: नारायण, IAST: Nārāyaṇa) is one of the forms and epithets of Vishnu. In this form, the deity is depicted in yogic slumber under the celestial waters, symbolising the masculine principle and associated with his role of creation.[1][2] He is also known as Purushottama, and is considered the Supreme Being in Vaishnavism.[3][4][5][6]
Etymology
[edit]Narayan Aiyangar states the meaning of the Sanskrit word 'Narayana' can be traced back to the Laws of Manu (also known as the Manusmriti, a Dharmaśāstra text),[7] which states:
The waters are called narah, (for) the waters are, indeed, the offspring of Nara; as they were his first residence (ayana), he thence is named Narayana.
— Chapter 1, Verse 10[8]
This definition is used throughout post-Vedic literature such as the Mahabharata and the Vishnu Purana.[7][9] 'Narayana' is also defined as the 'son of the primeval man',[10] and 'Supreme Being who is the foundation of all men'.[11]
- 'Nara' (Sanskrit नार) means 'water' and 'man'[12]
- 'Yana' (Sanskrit यान) means 'vehicle', 'vessel', or more loosely, 'abode' or 'home'[13]
L. B. Keny proposes that Narayana was associated with the Dravidian, and ultimately, the Indus Valley Civilisation, prior to his syncretism with Vishnu. To this end, he states that the etymology of the deity is associated with the Dravidian nara, meaning ‘water’, ay, which in Tamil means "to lie in a place", and an, which is the masculine termination in Dravidian languages. He asserts that this is also the reason why Narayana is represented as lying on a serpent in the sea. He quotes, "This Nārāyana of the Āryan pantheon seems to be the supreme being of the Mohenjo-Darians, a god who was probably styled Ān, a name still kept in Tamil literature as Āndivanam, the prototype of the historic Siva".[14][15][16]
Description
[edit]In the Vedas and the Puranas, Narayana is described as having the divine blackish-blue color of water-filled clouds, four-armed, holding a Padma (lotus), Kaumodaki gada (mace), Panchajanya shankha (conch), and Sudarshana chakra (discus).
Hinduism
[edit]
As stated in the epic Itihāsa, the Mahabharata:
I am Narayana, the Source of all things, the Eternal, the Unchangeable. I am the Creator of all things, and the Destroyer also of all. I am Vishnu, I am Brahma and I am Shankara, the chief of the gods. I am king Vaisravana, and I am Yama, the lord of the deceased spirits. I am Siva, I am Soma, and I am Kasyapa the lord of the created things. And, O best of regenerate ones, I am he called Dhatri, and he also that is called Vidhatri, and I am Sacrifice embodied. Fire is my mouth, the earth my feet, and the Sun and the Moon are my eyes; the Heaven is the crown of my head, the firmament and the cardinal points are my ears; the waters are born of my sweat. Space with the cardinal points are my body, and the Air is my mind...
...And, O Brahmana, whatever is obtained by men by the practice of truth, charity, ascetic austerities, and peace and harmlessness towards all creatures, and such other handsome deeds, is obtained because of my arrangements. Governed by my ordinance, men wander within my body, their senses overwhelmed by me. They move not according to their will but as they are moved by me.— Mahabharata (translated by Kisari Mohan Ganguli, 1883-1896), Book 3, Varna Parva, Chapter CLXXXVIII (188)[9]
As per texts like the Vishnu Purana, Bhagavata Purana, Garuda Purana, and the Padma Purana, Narayana is Vishnu himself, who incarnates in various avatars.
According to the Bhagavad Gita, he is also the "Guru of the Universe".[citation needed] The Bhagavata Purana declares Narayana as the Supreme Personality of Godhead, who engages in the creation of 14 worlds within the universe Brahma who is Deity of rajas-guna, himself sustains, maintains and preserves the universe as Vishnu by accepting sattva-guna.[citation needed] Narayana himself annihilates the universe at the end of Maha-Kalpa as Kalagni Rudra who is presiding deity of tamas-guna.
According to the Bhagavata Purana, Purusha Sukta, Narayana Sukta, and the Narayana Upanishad from the Vedas, he is the ultimate soul.
According to Madhvacharya, Narayana is one of the five vyuhas of Vishnu, which are cosmic emanations of God, in contrast to his incarnate avatars. Madhvacharya separates Vishnu's manifestations into two groups: Vishnu's vyuhas (emanations) and His avataras (incarnations).[17] The Vyuhas have their basis in the Pancharatras, a sectarian text that was accepted as authoritative by both the Vishishtadvaita and Dvaita schools of Vedanta. They are mechanisms by which the universe is ordered, was created, and evolves. Narayana possesses the chatur-vyuha aspects of Vasudeva, Sankarshana, Pradyumna, and Aniruddha, who evolve one after the other in the development of the universe. In the Mahabharata, Krishna is also synonymous with Narayana and Arjuna is referred to as Nara.[18] The epic identifies them both in plural 'Krishnas', or as part incarnations of the earlier incarnations of Vishnu, recalling their mystical identity as Nara-Narayana.[19]
Narayana (as Krishna) is also described in the Bhagavad Gita as having a universal form (Vishvarupa) which is beyond the ordinary limits of human perception or imagination.[20]
In the Narayana Sukta, Narayana is essentially the supreme force and/or essence of all: 'Nārāyaṇa parabrahman tatvam Nārāyaṇa paraha'.[21]
Narayana's eternal and supreme abode beyond the material universe is Vaikuntha, a realm of bliss and happiness called Paramapada, which means the final or highest place for liberated souls, where they enjoy bliss and happiness for eternity in the company of the supreme lord. Vaikuntha is situated beyond the material universe and hence, cannot be perceived or measured by material science or logic.[22] Sometimes, Kshira Sagara, where Narayana or Vishnu rests on Shesha in his reclining ananta shayana form,[23] is also perceived as Vaikuntha within the material universe.
The Śruti texts mention Narayana as the primordial being who was present even when Brahma and Ishana (Shiva) were not present. He is conceived as the Supreme Soul in the texts.[24]
Buddhism
[edit]The Mahāsamaya Sutta (DN 20) of the Pali Canon mentions a deity by the name Veṇhu (Sanskrit: Viṣṇu), though the text suggests that this name may also signify a class of deva. He also appears in the Veṇḍu Sutta (SN 2.12) as Veṇḍu where he addresses Gautama Buddha by celebrating the joy experienced by those who follow the Dhamma. He also makes brief mention of Manu.[25]
Mahayana Buddhism elaborates on the character of this deity, where he is often called Nārāyaṇa (Chinese: 那羅延天; Tibetan: མཐུ་བོ་ཆེ།) or more rarely, Narasiṃha (納拉辛哈) and Vāsudeva (婆藪天). Literature often depicts him as a Vajradhara (金剛力士). He is present in the Womb Realm Mandala and is among the twelve guardian devas of the Diamond Realm Mandala. He is associated with Śrāvaṇa in esoteric astrology.[26] His queen consort is Nārāyaṇī.[27] He is said to have been born from Avalokiteśvara's heart.[28] The Buddhas are sometimes described as having a firm vajra body like Nārāyaṇa.
The Yogācārabhūmi Śāstra describes him as having three faces with a greenish-yellow complexion. He holds a wheel in his right hand and rides upon a garuḍa. Chapter 6 of the Yiqiejing Yinyi explains that he belongs to the Kāmadhātu and is venerated for the acquisition of power. Chapter 41 adds that he has eight arms that wield various "Dharma weapons" (dharmāyudha) with which he subjugates the asuras.
He appears as an interlocutor in several Mahayana sutras, including the Kāraṇḍavyūha Sūtra, Sarvapuṇyasamuccayasamādhi Sūtra and the Nārāyaṇaparipṛcchā Dhāraṇī.
He is also mentioned in several places in the Lalitavistara Sūtra, one of the Sutras that describe the life of Gautama Buddha. It is said that because the Buddha is "endowed with the great strength of Nārāyaṇa, he is called the great Nārāyaṇa himself."
The Chinese Manichaean manuscript Moni Guangfo, a syncretic religious text incorporating both Buddhist and Manichaean elements, considers Nārāyaṇa (Chinese: 那羅延; pinyin: Naluoyan) to be one of the Five Buddhas, with the other buddhas being Zoroaster, Śākyamuni, Jesus, and Mani.[29]
Jainism
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2023) |
Balabhadra and Narayana are mighty half-brothers, who appear nine times in each half of the time cycles of the Jain cosmology and jointly rule half the earth as half-chakravarti. Ultimately Prati-naryana is killed by Narayana for his unrighteousness and immorality. Narayana are extremely powerful and are as powerful as 2 Balabhadras. Chakravartins are as powerful as 2 Narayanas. Hence Narayanas become half-chakravartins. Tirthankaras are much more powerful than Chakravartins. In Jain Mahabharata, there is a friendly duel between cousin brothers Neminatha (Tirthankara) and Krishna (Naryana) in which Neminath lost to Krishna without any effort at all. There is also a story of Neminatha lifting the conch of Krishna and blowing it without any effort. The Jain Mahabharata describes Krishna's conflict with Jarasandha, who he kills.
Literature
[edit]Narayana is hailed in certain parts of the Vedas like the Narayana Suktam and the Vishnu Suktam. He is also hailed in selective Vaishnava Upanishads like the Narayana Upanishad, Mahanarayana Upanishad, and the Nrisimha Tapaniya Upanishad.[30]
The Padma Purana relates an episode where Narayana grants Rudra (Shiva) a boon. The destroyer deity seeks two boons. Firstly, he wishes to be the greatest of the devotees of Narayana, as well as bearing the reputation of the same throughout the world. Secondly, he desires the ability to offer salvation to whoever seeks refuge in him.[31]
The prowess of Narayana is described in the Ramayana:[32]
Narayana, like unto a luminous cloud, with his excellent shafts loosed from His bow, as so many lightning strokes, exterminated those rangers of the night with their hair dishevelled and streaming in the wind. Their parasols broken, their rich apparel torn by the shafts, their entrails ripped open, their eyes wide with fear, those warriors, throwing away their arms, fell into a frenzy of terror. Resembling elephants attacked by a lion, those night-rangers with their mounts emitted cries whilst fleeing from that Primeval Lion [i.e., Vishnu’s incarnation as Nrsimha—half man, half lion], who pursued them.
Ramanuja's prayer of surrender to Narayana in the Sharanagati Gadyam of the Tiruvaymoli was and is significant to his Sri Vaishnava adherents, as it became a model prayer for future generations. In this prayer, Ramanuja describes Narayana to be the "beloved consort of Sri and of Bhumi and Nila". He is stated to reside in his abode of Vaikuntha, where he assumes the role of the creation, preservation, as well as the destruction of the universe. Narayana is extolled to be the same as the Ultimate Reality, Brahman. He is regarded to be the refuge of all creation, the master of spiritual as well as material entities, as well as the dispeller of the miseries of his devotees. He ends his prayer by saluting Narayana and his consort Sri, to whom he surrenders to his "lotus-like feet".[33]
-
Narayan Temple on Narayanhiti palace premises, Kathmandu, Nepal
-
Oldest Sridhar Narayan statue at Naksaal, Kathmandu
-
The bow of Royal Barge Narai Song Suban HM Rama IX of Thailand, it carved an image of Narayana riding a Garuda
-
Sculpture of Narayana around 14/15th century, found at the Devasathan, inner Bangkok, Thailand
-
Sculpture of Narayana ride a Garuda built in Khmer art style in front of InterContinental Bangkok, Phloen Chit Road, it is one of the most respected Hindu shrines in the Ratchaprasong neighbourhood alike Erawan Shrine
-
Drawing of sleeping Narayana on Sheshanaga while the four-headed Brahma springs from his navel
-
Statue of Narayana in Thai art style stands on Mount Mandara within Suvarnabhumi Airport, Samut Prakan, Thailand
-
Khmer lintel depicting Narayana sleeping upon the Sheshanaga in the middle of Milky Ocean, Bangkok National Museum
See also
[edit]| Vyūhas | Image | Attributes | Symbol[37][38] | Direction | Face | Concept | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narayana Vishnu |
Vāsudeva | Chakra Wheel Gadā Mace Shankha Conch |
Garuda Eagle | 
|
East | Saumya (Placid/ benevolent) |
Jṅāna Knowledge | ||
| Samkarsana | Lāṅgala Plough Musala Pestle Wine glass |
Tala Fan palm | 
|
South | Simha Lion | Bala Strength | |||
| Pradyumna | Cāpa Bow Bāṇa Arrow |
Makara Crocodile | West | Raudra Kapila | 
|
Aiśvaryā Sovereignty | |||
| Aniruddha | Carma Shield Khaḍga Sword |
Ṛṣya (ऋष्य) White-footed antelope | North | Varaha Boar | Śakti Power | ||||
References
[edit]- ^ Leeming, David (17 November 2005). Oxford Companion to World Mythology. Oxford University Press. p. 278. ISBN 978-0-19-028888-4.
- ^ "Invoking Auspiciousness [Chapter 1]". 14 August 2014.
- ^ John Clifford Holt (2008). The Buddhist Viṣṇu: Religious Transformation, Politics, and Culture. Motilal Banarsidass Publishers. p. 268. ISBN 9788120832695.
- ^ Jon Paul Sydnor (29 March 2012). Ramanuja and Schleiermacher: Toward a Constructive Comparative Theology. ISD LLC. p. 110. ISBN 9780227900352.
- ^ C. Mackenzie Brown (29 August 1990). The Triumph of the Goddess: The Canonical Models and Theological Visions of the Devi-Bhagavata Purana. SUNY Press. p. 28. ISBN 9780791403648.
- ^ Peter Clarke; Friedhelm Hardy; Leslie Houlden; Stewart Sutherland (14 January 2004). The World's Religions. Routledge. p. 748. ISBN 9781136851858.
- ^ a b Narayan Aiyangar (1901). Essays on Indo Aryan Mythology. pp. 196.
- ^ "The Laws of Manu I". www.sacred-texts.com. Retrieved 7 December 2019.
- ^ a b "The Mahabharata, Book 3: Vana Parva: Markandeya-Samasya Parva: Section CLXXXVIII". www.sacred-texts.com. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ "Monier-Williams Sanskrit-English Dictionary -- n". faculty.washington.edu. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ Harivansh, Adhyay 88 shlock 44, also, Manu Smruti 1:10 " The Law Code of Manu", Published by Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-280271-2, page 11
- ^ "Sanskrit Dictionary for Spoken Sanskrit: 'nara'". spokensanskrit.org. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ "Sanskrit Dictionary for Spoken Sanskrit 'yana'". spokensanskrit.org. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- ^ Klostermaier, Klaus K. (1 January 2006). Mythologies and Philosophies of Salvation in the Theistic Traditions of India. Wilfrid Laurier Univ. Press. pp. 70–71. ISBN 978-0-88920-743-1.
- ^ The Book of Avatars and Divinities. Penguin Random House India Private Limited. 21 November 2018. ISBN 978-93-5305-362-8.
- ^ Krishna, Nanditha (June 2010). The Book of Vishnu. Penguin Books India. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-14-306762-7.
- ^ Ghosh, A. (2 March 2009). "Krishna: A Sourcebook. Edited by Edwin F. Bryant". The Journal of Hindu Studies. 2 (1): 124–126. doi:10.1093/jhs/hip002. ISSN 1756-4255.
- ^ Vaisnavism Saivism and Minor Religious Systems, Ramkrishna Gopal Bhandarkar. Published by Asian Educational Services, p.46.
- ^ Hiltebeitel, Alf (1990). The ritual of battle: Krishna in the Mahābhārata. Albany, N.Y: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-0249-5. p61
- ^ Prabhupada, AC Bhaktivedanta. "Bhagavad-gita As It Is Chapter 11 Verse 3". vedabase.net. Archived from the original on 15 May 2008. Retrieved 10 May 2008. "see the cosmic manifestation"
- ^ "॥ नारायणसूक्तम् सार्थ ॥ - .. Narayana Sukta .. - Sanskrit Documents". sanskritdocuments.org. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ "Sapthagiri". Archived from the original on 15 May 2007. Retrieved 21 May 2007.
- ^ DK (2 June 2008). Signs & Symbols: An Illustrated Guide to Their Origins and Meanings. Dorling Kindersley Limited. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-4053-3648-2.
- ^ "Upanishads".
- ^ "SN 2.12: With Vishnu —Bhikkhu Sujato". SuttaCentral. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ^ "那羅延". Digital Dictionary of Buddhism. 2009. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ^ The Vairocanābhisaṃbodhi Sūtra (PDF). Translated by Giebel, Rolf W. BDK America, Inc. 2005.
- ^ Roberts, Peter Alan; Tulku Yeshi (2013). "The Basket's Display". 84000: Translating the Words of the Buddha. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
- ^ Ma, Xiaohe; Wang, Chuan (9 July 2018). "On the Xiapu Ritual Manual Mani the Buddha of Light". Religions. 9 (7). MDPI AG: 212. doi:10.3390/rel9070212. ISSN 2077-1444.
- ^ "Narayanastra – Defending Vaishnavism as the supreme Vedic position". narayanastra.blogspot.in. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ www.wisdomlib.org (26 September 2019). "Nārāyaṇa Grants Boons to Rudra [Chapter 2]". www.wisdomlib.org. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ www.wisdomlib.org (27 September 2020). "The Combat between Vishnu and the Rakshasas [Chapter 7]". www.wisdomlib.org. Retrieved 12 August 2022.
- ^ Makarand Joshi (1989). The Tamil Veda Pillan Interpretation Of Tiruvaymoli J Carman And V Narayanan. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Atherton, Cynthia Packert (1997). The Sculpture of Early Medieval Rajasthan. Brill. p. 78. ISBN 978-90-04-10789-2.
- ^ A Comprehensive History of India: pt. 1-2. A.D. 300-985. Orient Longmans. 1982. p. 866.
- ^ Parlier-Renault, Edith (2007). Temples de l'Inde méridionale: VIe-VIIIe siècles. La mise en scène des mythes. Presses Paris Sorbonne. pp. 38–42. ISBN 978-2-84050-464-1.
- ^ "A shrine of Aniruddha, the fourth of the 'vyuhas', which had within its precincts a 'rsyadhvaja', i. e. a column bearing on its top the figure of a 'rsya' or a white antelope which was his characteristic 'lanchana'." in Journal of the Indian Society of Oriental Art. Indian Society of Oriental Art. 1937. p. 16.
- ^ Gupta, Vinay K. "Vrishnis in Ancient Literature and Art". Indology's Pulse Arts in Context, Doris Meth Srinivasan Festschrift Volume, Eds. Corinna Wessels Mevissen and Gerd Mevissen with Assistance of Vinay Kumar Gupta: 80–81.